The Regency era in India, spanning from 1811 to 1820, marked a period of significant political and social change in the subcontinent. Under the rule of the British East India Company, India experienced a shifting landscape of governance, trade, and cultural exchange. This article delves into the complexities of the Regency era in India, exploring the key events, figures, and developments that shaped this pivotal time in history.
Step Into the World of Cheryl Bolen
Dive into the enchanting stories of love, intrigue, and elegance set in the Regency Era. Cheryl Bolen's novels offer timeless romance and captivating tales that will leave you wanting more.
Explore Cheryl Bolen's Books Now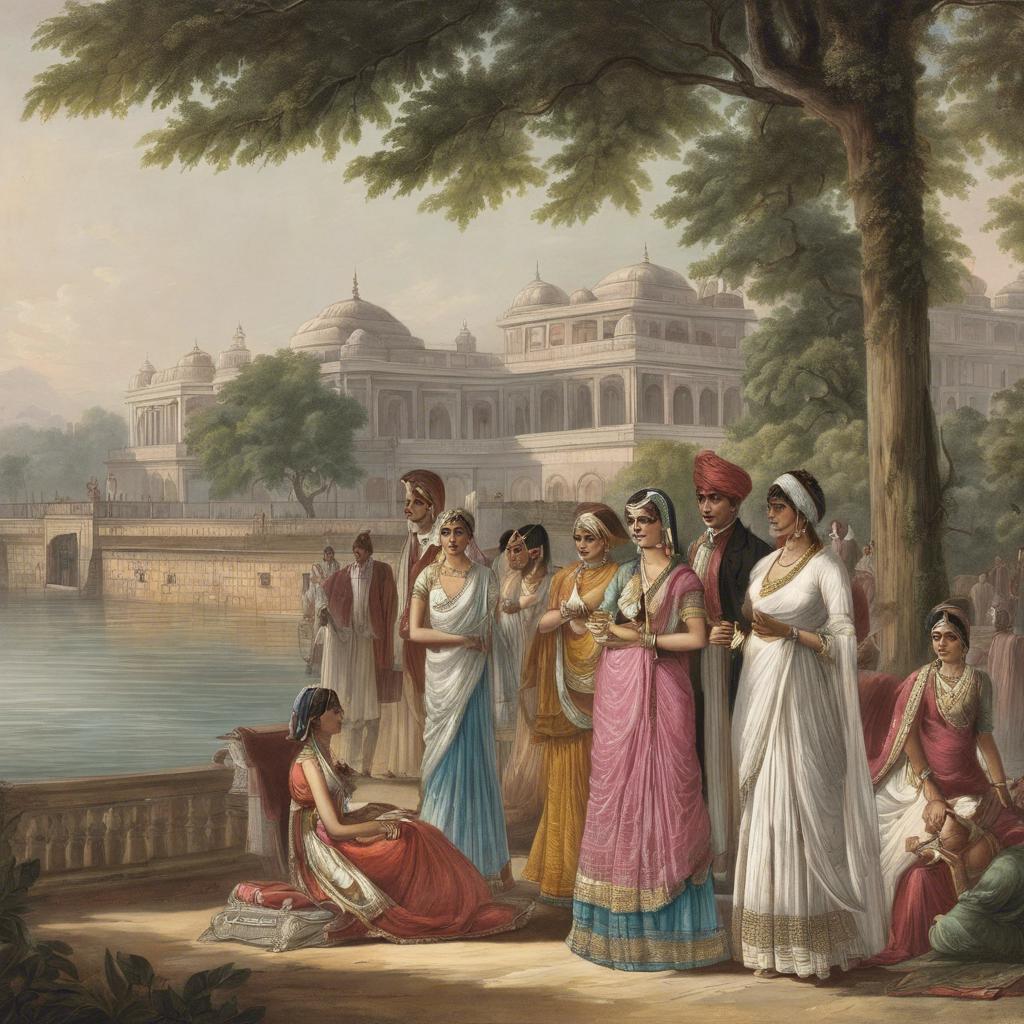
Overview of Regency Era India
The Regency Era in India, spanning from 1798 to 1837, was a period of significant political and social change. This era was marked by the rise of the British East India Company as a dominant force in India, following the decline of Mughal power. The Company’s control over vast territories gave it immense influence over the Indian subcontinent.
During the Regency Era, British influence in India extended beyond political and economic spheres. This period saw the spread of Western education and ideas, leading to the emergence of a new class of Indian intellectuals who were exposed to European philosophies and literature. The British also introduced modern administrative systems and infrastructure projects, impacting the social and cultural fabric of Indian society.
The Regency Era in India was characterized by both cooperation and conflict between the British and Indian rulers. While some Indian princes collaborated with the British to maintain their power and privileges, others resisted the colonial rule through rebellions and uprisings. This period laid the foundation for the Indian independence movement, as the subjugated people of India began to assert their rights and strive for self-governance.
Economic Impact of British Rule in Regency Era India
The was profound and far-reaching. One of the most significant changes was the transformation of the Indian economy from a largely agrarian society to a more industrialized one. This shift was characterized by the establishment of factories, railways, and other modern infrastructure by the British, which helped to stimulate economic growth in the region.
Additionally, British rule in India led to the introduction of new cash crops such as tea, coffee, and cotton, which were grown on a large scale for export to Britain and other parts of the world. This not only boosted India’s agricultural output but also contributed to the global economy by providing raw materials for British industries.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that the economic benefits of British rule were not evenly distributed. The policies implemented by the British often favored British industries and merchants at the expense of Indian producers. These unequal trade practices and oppressive taxation policies not only hindered the development of Indian industries but also exacerbated poverty and inequality among the Indian population.
Social Changes and Cultural Influences in Regency Era India
In the Regency Era India, significant social changes and cultural influences shaped the landscape of the country. One of the most prominent aspects of this period was the emergence of a new class of wealthy Indians who embraced Western customs and lifestyles. This led to a blending of traditional Indian values with European ideals, creating a unique cultural fusion.
Key :
- The influence of British colonial rule on Indian society, leading to the adoption of English language, fashion, and etiquette among the elite.
- The spread of education and literacy, which expanded the intellectual and cultural horizons of the Indian population.
- The rise of Indian nationalism and the push for social reform, challenging traditional customs and hierarchies.
Notable figures of the Regency Era in India:
| Name | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Raja Ram Mohan Roy | Prominent social reformer who advocated for women’s rights and the abolition of Sati. |
| Lord Cornwallis | Governor-General who implemented administrative reforms in India, shaping the British colonial legacy. |
| Begum Hazrat Mahal | Revolutionary leader who fought against British rule during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. |
Recommendations for Further Study on Regency Era India
Further Study Recommendations
For those interested in delving deeper into the fascinating history of Regency Era India, there are several avenues of study worth exploring:
- Investigate the impact of British colonial rule on Indian society, politics, and economy during the Regency period.
- Explore the cultural exchange between India and Britain, focusing on art, literature, and architecture from the era.
- Examine the role of Indian women in society and politics, shedding light on their experiences and contributions during this time.
| Recommended Books |
|---|
| “White Mughals” by William Dalrymple |
| “The Last Mughal” by William Dalrymple |
| “The Hindus: An Alternative History” by Wendy Doniger |
By exploring these topics and delving into these recommended readings, you can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and nuances of Regency Era India.
Insights and Conclusions
the Regency Era in India was a time of immense change and development in various aspects of society. From the introduction of new ideas and technologies to the impact of British colonial rule, this period in Indian history laid the foundation for the modern nation we see today. The legacy of the Regency Era continues to shape India’s culture, politics, and economy, reminding us of the complexities and transformations that occurred during this pivotal time in history. As we reflect on the triumphs and challenges of the Regency Era, we gain a deeper understanding of the rich tapestry of India’s past and the enduring impact it has on the present.


